EVPN MP-BGP: fabric clos best-practices
11.03 2024 | by massimilianoEVPN (Ethernet Virtual Private Network) collega un gruppo di users sites usando un virtual bridge layer 2; Tratta indirizzi MAC […]
EVPN (Ethernet Virtual Private Network) collega un gruppo di users sites usando un virtual bridge layer 2;
Tratta indirizzi MAC come address ruotabili e distribuisce queste informazioni via MP-BGP;
Utilizzato in ambienti Data Centers multi-tenancy con end-point virtualizzati; supporta encapsulamento VXLAN e lo scambio di indirizzi IP host e IP-Prefix.
EVPN MP-BGP control plane
- informazioni layer 2 (MAC address) e layer 3 (host IP address) imparate localmente da ogni VTEP sono propagate ad altri VTEP permettendo funzionalità di switching e routing all’interno della stessa fabbrica;
- le routes sono annunciate tra VTEP attraverso route-target policy;
- utilizzo di VRF e route-distinguisher per routes/subnet;
- le informazioni layer 2 sono distribuite tra VTEP con la funzionalità di ARP cache per minimizzare il flooding;
- le sessioni L2VPN EVPN tra VTEP possono essere autenticate via MD5 per mitigare problematiche di sicurezza (Rogue VTEP)
In genere un data centers IaaS costruito su una architettura Spine-Leaf utilizza per migliorare le sue performance di raggiungibilità layer 2 e 3 un processo ECMP (Equal Cost Multi Path) via IGP.
In caso di crescita della Fabric con la separazione multi-tenant, si può pensare a meccanismi di scalabilità come il protocollo BGP e scegliere se utilizzare Internal-BGP oppure external-BGP in considerazione anche di meccanismi ECMP molto utili in ambienti datacenters
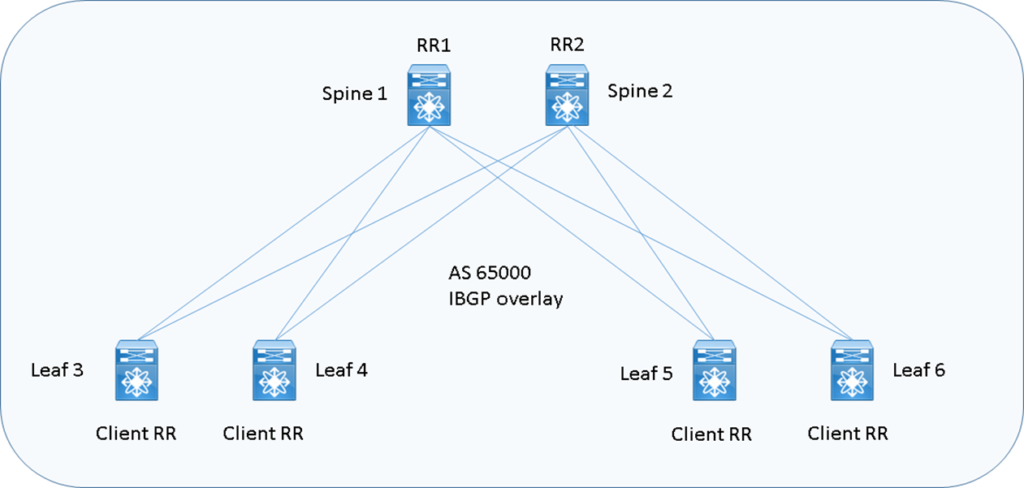
IBGP richiede sessioni tra tutti i PE VTEP e l’impiego di Router Reflector aiuta molto in termini di scalabilità delle sessioni configurati a livello Spine; questo tipo standard di soluzione, in ogni caso, riflette solo il best-single-prefix verso i loro client ed nella soluzione di utilizzare ECMP bisogna configurare un BGP add-path feature per aggiungere ECMP all’interno degli annuncia da parte dei RRs
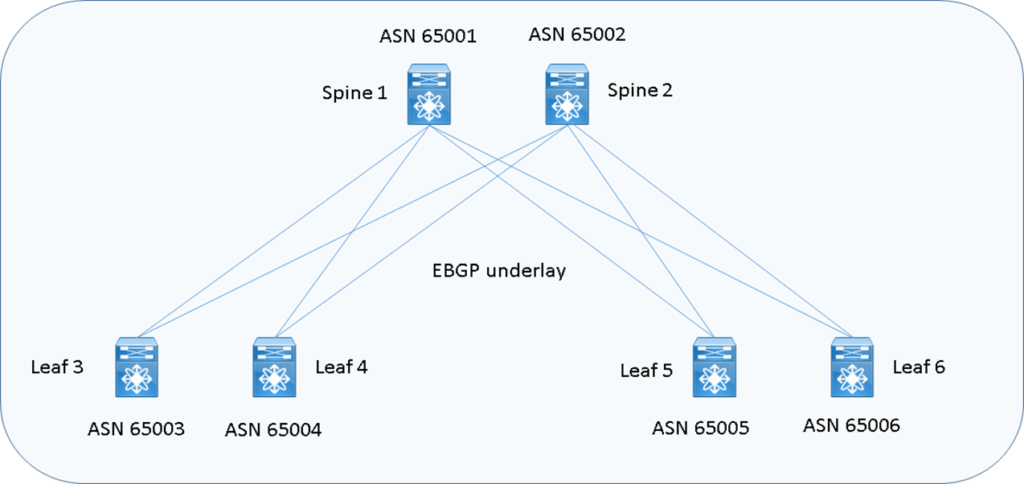
EBGP, invece, supporta ECMP senza add-path ed è semplice nella sua tradizionale configurazione; con EBGP ogni devices della Fabric utilizza un proprio AS (Autonomous System)
MP-BGP EVPN utilizza due routing advertisement:
- Route type 2: usato per annunciare host MAC ed IP address information per gli endpoint direttamente collegati alla VXLAN EVPN Fabric, ed anche trasportare extended community attribute, come route-target, router MAC address e sequence number

- Route type 5: annuncio di IP Prefix oppure host routes (loopback interface) ed anche trasporto di extended community attribute, come route-target, router MAC address e sequence number

EVPN E-BGP and ASN underlay design
EVPN I-BGP and ASN underlay design
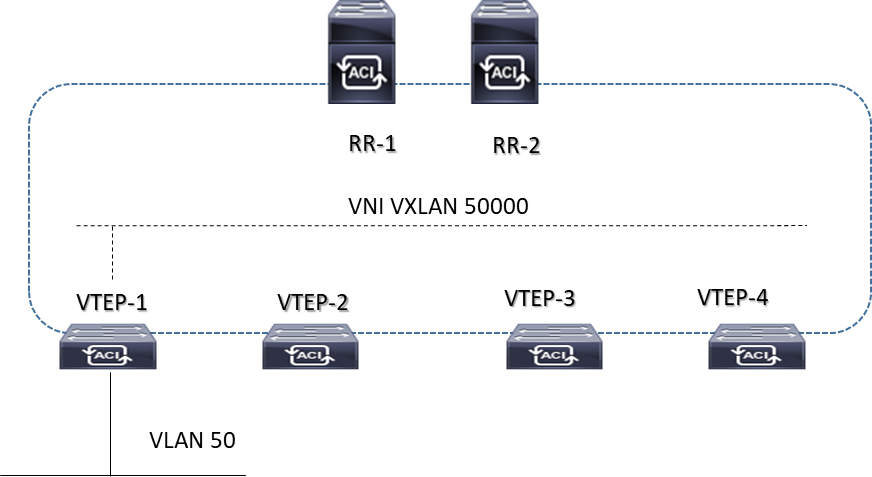
Esempio di configurazione EVPN IBGP VTEP VXLAN

feature bgp
feature nv overlay # enable VTEP (required on Leaf or Border)
fature nv overlay evpn # enable EVPN control-plane in BGP
@ only on LEAF
interface nve1 # enable interface VTEP
source-interface loopback0 # enable source interface with loopback
host-reachability protocol bgp # enable BGP for host reachability
# SPINE RR1
router bgp 65000
router-id 192.168.1.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 192.168.1.10 remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community both
route-reflector client
# LEAF VTEP-1
router bgp 65000
router-id 192.168.1.10
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 192.168.1.1 remote-as 65000
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community both
# Mapping IEEE 802.1q vlan-id TO VXLAN VNI
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
vlan 50
vn-segment 50000
evpn
vni 50000 l2
rd auto # RD is default calculated as VNI:BGP Router ID
route-target import auto # RT is default calculated as BGP AS:VNI
route-target export auto
!
interface nve1
source-interface loopback0
host-reachability protocol bgp
member vni 50000
mcast-group 239.239.239.10
suppress-arp
# Define VLAN for VRF routing instances
vlan 50
vn-segment 50000
interface vlan 50
no shutdown
mtu 9216
vrf member VRF-A
ip forward
!
vrf context VRF-A
vni 50000
rd auto
address-family ipv4unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
# Define VLAN 50 and 60 and Distributed IP Anycast Gateway
features interface-vlan
fabric-forwarding anycast-gateway-mac < mac-address > # un MAC address per VTEP; tutti i VTEP dovrebbero avere lo stesso MAC Address
vlan 50
vn-segment 50000
vlan 60
vn-segment 60000
!
interface vlan 50
no shutdown
mtu 9216
vrf member VRF-A
ip address 50.50.50.1/24 tag 123
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
!
interface vlan 60
no shutdown
mtu 9216
vrf member VRF-A
ip address 60.60.60.1/24 tag 123
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
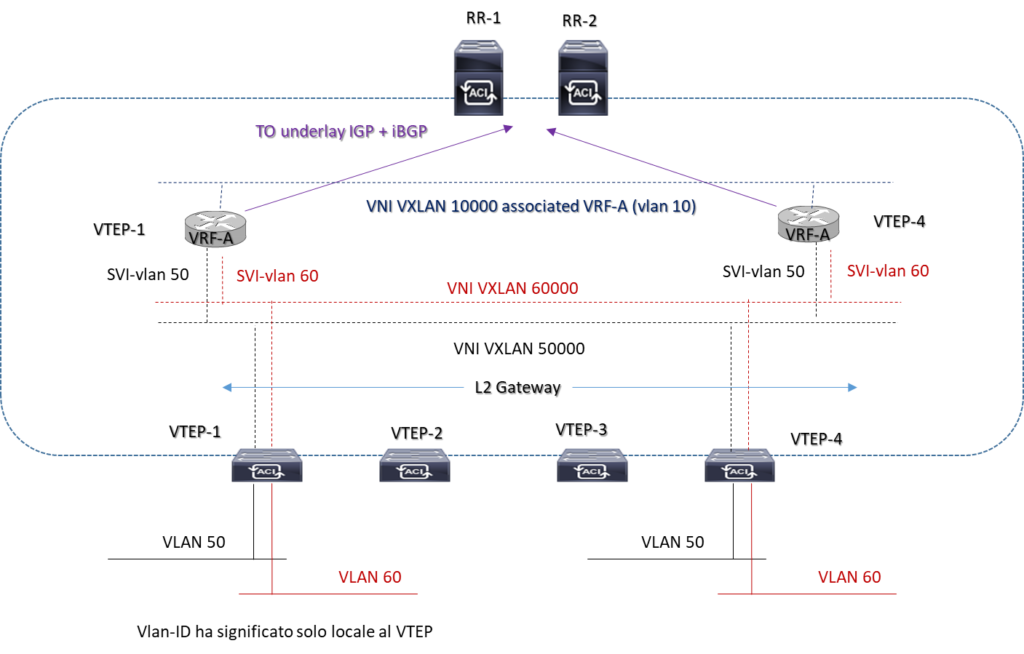
EVPN IBGP Routing on VXLAN
vlan 10 # vlan 10 is used as Layer 3 VNI to route inter-vlan routing
vn-segment 10000
!
interface vlan 10 # Layer 3 VNI associated interface vlan does not have an ip address
vrf member VRF-A
no shutdown
!
interface nve1
source-interface loopback0
host-reachability protocol bgp
member vni 50000
mcast-group 239.239.239.10
suppress-arp
member vni 10000 associate-vrf
!
member vni 60000
mcast-group 239.239.239.11
suppress-arp
member vni 10000 associate-vrf
!
route-map RED-SUBNET permit 10
match 123
!
router bgp 65000
vrf VRF-A
advertise l2vpn evpn
redistribuite direct route-map RED-SUBNET
maximum-path ibgp 2
EVPN IBGP with OSPF UNDERLAT configuration reachability loopback on VTEP1

VTEP1:
feature ospf
feature pim
!
ip pim rp-address 192.168.1.1 group-list 224.0.0.0/4
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
!
interface ethernet 1/2
description to-SPINE
no switchport
ip address 10.1.1.2/30
ip route ospf UNDERLAY area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
interface loopback 0
description «loopback for BGP»
ip address 192.168.1.10/32
ip route ospf UNDERLAY area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
router ospf UNDERLAY